Bitcoin btc
Collective Shift Analysis
To see Collective Shift’s analysis, sign up for Insider or Pro!
Bitcoin Summary
Bitcoin is a digital payments system and form of cryptocurrency invented in 2008 and launched in 2009. It’s the world’s first widely used cryptocurrency, and its creation follows several failed attempts at digital forms of peer-to-peer money since the 1980s.
With Bitcoin, a user can transfer money to anyone from anywhere in the world without an intermediary.
It is a new monetary asset class where transactions are recorded on a ledger. This ledger is the Bitcoin blockchain and uses a system—proof of work (PoW)—where miners validate all transactions are legitimate and maintain the ledger.
All transactions ever recorded on this blockchain are visible to anyone. As a result of the vast amount of computing power it takes to ‘mine‘ blocks of Bitcoin, some describe it as ‘digital gold’ for its hard-capped 21M supply.
Creation
The creator of Bitcoin goes by the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto, whose identity remains unknown.
Satoshi published the Bitcoin whitepaper in Oct. 2008, which described a way to create a monetary network without the need for a central authority.
The timing is interesting, given the launch happened following the second biggest financial crisis since the Great Depression (the Global Financial Crisis). Satoshi left a news article inside the Bitcoin blockchain on its genesis block, pointing to a deeper meaning for Bitcoin as a non-state-issued private currency that cannot be willfully printed.
What Makes Bitcoin Valuable?
The current system of money and payments works pretty well in stable, developed countries. Even though central banks and governments control these currencies, anything radical and extreme rarely occurs.
But if you’re one of the billions living in countries that are relatively less stable and developed, this can be a very real occurrence.
Transactions can happen without the oversight or control of banks or governments. This means for 1.7 billion adults worldwide who are either unbanked or live in corrupt countries, they can manage their finances independently.
Bitcoin is a digital currency solution, transgressing borders and establishing an equal, common monetary system.
A problem Bitcoin aimed to solve is the fact that despite so much of our lives having transitioned online, money still remains in physical form and is relatively archaic. Bitcoin solves this issue by making it easier to almost instantly transfer value across its platform, unlike banks which take much more time to move foreign currencies.
Finally, the thing that makes Bitcoin so valuable is a select few cannot change Bitcoin or increase it’s supply. It gives Bitcoin predictability and trust, unlike the host of current fiat currencies (such as the EURO or USD), where money can be easily debased or printed.
BTC Utility
Bitcoin is underpinned by its native cryptocurrency, bitcoin (BTC). There is a fixed maximum supply of 21 million BTC, with over 90% in circulation.
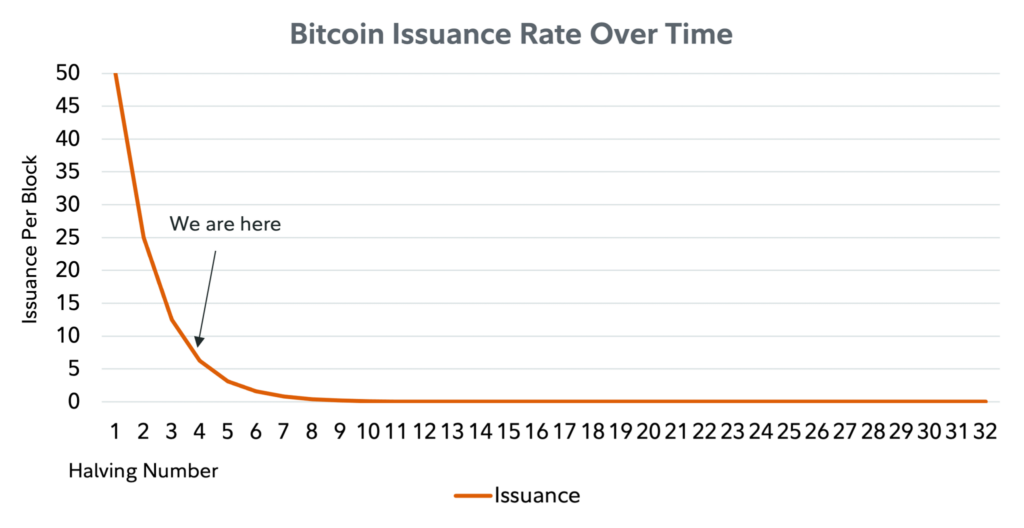
More BTC is slowly released every 10 minutes to so-called ‘miners’, who earn BTC for operating the Bitcoin blockchain.
Every 4 years, the BTC reward is halved until there’s no more BTC to be rewarded sometime in the year 2140. The current reward is 6.25 BTC, but will halve to 3.125 in April 2024.
BTC has multiple use cases and benefits:
- Store of value: Increasingly, BTC is seen as a ‘digital gold’ for storing and maintaining wealth. This is becoming increasingly important as governments and central banks tackle high inflation and quantitative easing (QE).
- Peer-to-peer monetary system and currency: BTC can be used to buy and sell goods and services or send value between two parties. BTC is fundamentally an open-source, peer-to-peer monetary system.
- Money free from censorship or tampering: Banks and governments cannot directly control or move an individual’s Bitcoin (as long as it’s self-custody) if they do not have access to the private keys.