Ethereum eth
Collective Shift Analysis
To see Collective Shift’s analysis, sign up for Insider or Pro!
Ethereum Summary
Ethereum is an open-source, decentralised computing infrastructure. It uses a global network of computers that are connected via a publicly distributed network called a blockchain.
Ethereum is best known for supporting smart contracts—something that greatly differentiates itself from Bitcoin. Ethereum lets developers create decentralised applications (apps) available to anyone with a web wallet anywhere in the world.
For example, to create financial applications (i.e. DeFi), games, store value, NFTs or important digital assets. Think of Ethereum as the network or app store on which any developer can deploy an app.
History of Ethereum
Vitalik Buterin published Ethereum’s whitepaper in November 2013. After being built by Buterin and other developers, the first Ethereum block was mined in July 2015. Ethereum went through a contentious hard fork in 2016, resulting in Ethereum Classic—the original, unaltered history of the Ethereum network. The network was seeded by an initial coin offering (ICO) in mid-2014, which raised ~$18M worth of BTC.
Upgrading Ethereum
Ethereum is evolving to solve scalability and congestion issues that have been plaguing the network’s ability to meet demand.
Previously touted as ‘Ethereum 2.0’, it is an ongoing series of core implementations to increase network capacity, cater to more transactions and improve environmental efficiency. This is a continual process that will happen over the next few years, changes include:
- Moving from proof of work (PoW) to proof of stake (PoS). [✅Occured in September 2022]
- Embracing scaling solutions such as roll-ups to house the bulk of transactions—with the Ethereum base layer to become the settlement layer. [✅Occured in April 2024]
- Implement dank sharding to scale its L2 roadmap. [➖Ongoing].
Ethereum is pursuing a “layered’ approach to scalability. Simply, Ethereum is creating software that allows blockchains and networks to build on top of it, inheriting its security. The idea is to move the bulk of activity away from Ethereum’s main chain (known as the L1) to alternative networks that are inherent in its security (known as L2s, such as Arbitrum) so it can achieve sufficient scale and reduce gas fees.
ETH Token Utility
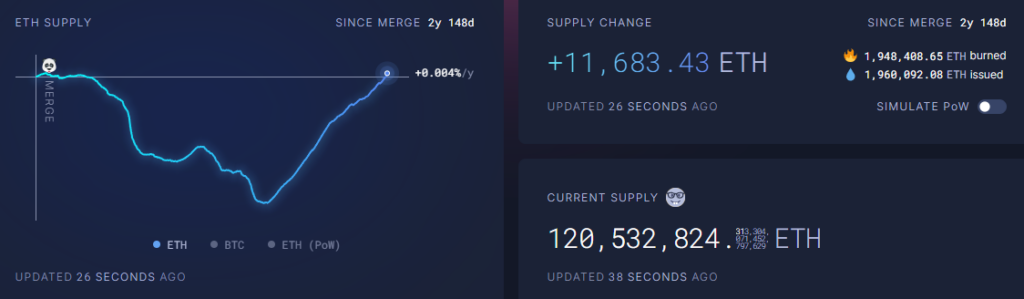
Ethereum’s native cryptocurrency is ether (ETH). Unlike cryptocurrencies like BTC, ETH has no maximum supply but changes based on several factors, including network usage and the amount of ETH staked. As of early 2025, the circulating supply is roughly 120 million ETH.
ETH is the economic incentive used to reward those who validate transactions on the blockchain. Other use cases for ETH are listed below.
- Transaction fees: ETH is required to send transactions or build applications. (See: What Is Gas on Ethereum?)
- Store of value: As ETH is an important resource for running the blockchain, many users may choose to buy and hold it as it becomes more scarce and a required asset for buying gas.
- Economic incentive: ETH is primarily the economic incentive for stakers to secure and validate the blockchain. Without ETH, there’s no incentive for users to secure the chain.
Anyone can track the supply of ETH at ultrasound.money